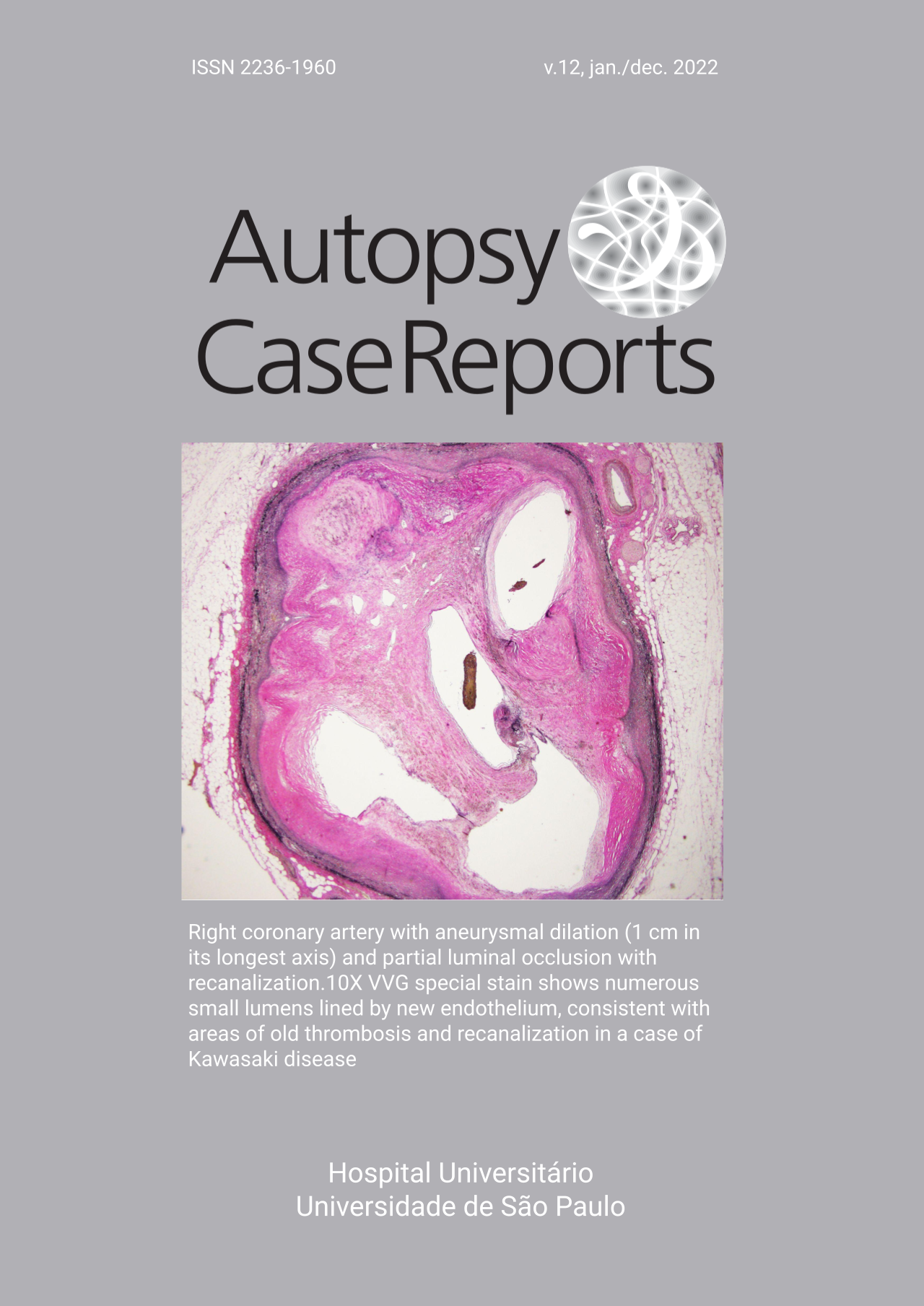
Adult-onset Still's disease after ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine: a possible association
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.4322/acr.2021.403Keywords:
Adenovirus Vaccines, COVID-19 Vaccines, Still's Disease, Adult-OnsetAbstract
With emergent Sars-Cov-2, a highly transmissive virus that caused millions of deaths worldwide, the development of vaccines became urgent to combat COVID-19. Although rare, important adverse effects had been described in a hypothetical scenario of immune system overstimulation or overreaction. Still’s disease is a rare inflammatory syndrome of unknown etiology. It manifests as a cytokine storm, mainly IL-18 and IL-1β, and presents itself with fever spikes, joint pain, maculopapular evanescent salmon-pink skin rash, and sore throat, among other symptoms. Here, we report a case of a 44-year-old healthy male who developed adult-onset Still’s disease (AOSD) with atypical symptoms after both doses of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine with 3 months of dose interval. The medical team suspected Still's disease and started prednisone 1 mg/kg (40mg). The next day the patient showed a marked improvement in articular and chest pains and had no other fever episodes. Therefore, he was discharged to continue the treatment in outpatient care. On the six-month follow-up, the patient was free of complaints, and the progressive corticoid withdrawal plan was already finished.
Downloads
References
Liu Y, Sawalha AH, Lu Q. COVID-19 and autoimmune diseases. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2021;33(2):155-62. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/BOR.0000000000000776. PMid:33332890.
Sharabi A, Shiber S, Molad Y. Adult-onset Still’s disease following mRNA COVID-19 vaccination. Clin Immunol. 2021;233:108878. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.clim.2021.108878. PMid:34763089.
Magliulo D, Narayan S, Ue F, Boulougoura A, Badlissi F. Adult-onset Still’s disease after mRNA COVID-19 vaccine. Lancet Rheumatol. 2021;3(10):e680-2. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S2665-9913(21)00219-8. PMid:34316726.
Leone F, Cerasuolo PG, Bosello SL, et al. Adult-onset Still’s disease following COVID-19 vaccination. Lancet Rheumatol. 2021;3(10):e678-80. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S2665-9913(21)00218-6. PMid:34316728.
Gerfaud-Valentin M, Jamilloux Y, Iwaz J, Sève P. Adult-onset Still’s disease. Autoimmun Rev. 2014;13(7):708-22. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2014.01.058. PMid:24657513.
Tomaras S, Goetzke CC, Kallinich T, Feist E. Adult-onset Still’s disease: clinical aspects and therapeutic approach. J Clin Med. 2021;10(4):733. http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/jcm10040733. PMid:33673234.
Kawasaki T, Ooka S, Mizushima M, et al. COVID-19 and adult-onset Still’s disease as part of hyperferritinemic syndromes. Mod Rheumatol Case Rep. 2022;6(1):101-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/mrcr/rxab032. PMid:34592766.
Pascolini S, Vannini A, Deleonardi G, et al. COVID-19 and immunological dysregulation: can autoantibodies be useful? Clin Transl Sci. 2021;14(2):502-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/cts.12908. PMid:32989903.
Talotta R. COVID-19 RNA-based vaccines put at risk of immune-mediated diseases? In reply to “potential antigenic cross-reactivity between SARS-CoV-2 and human tissue with a possible link to an increase in autoimmune diseases”. Clin Immunol. 2021;224:108665. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.clim.2021.108665. PMid:33429060.
Getts MT, Miller SD. 99th Dahlem conference on infection, inflammation and chronic inflammatory disorders: triggering of autoimmune diseases by infections. Clin Exp Immunol. 2010;160(1):15-21. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2249.2010.04132.x. PMid:20415846.
Yoshioka K, Fujimoto S, Oba H, Minami M, Aoki T. Onset of adult-onset Still’s disease following influenza vaccination. Mod Rheumatol. 2011;21(4):432-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/s10165-011-0418-7. PMid:21327453.
Sato T, Takeo N, Matsuda-Hirose H, Abe K, Nishida H, Hatano Y. Adult-onset Still’s disease following pneumococcal vaccination. Eur J Dermatol. 2021. In press. PMid:34427562.
Fujinami RS, von Herrath MG, Christen U, Whitton JL. Molecular mimicry, bystander activation or viral persistence: infections and autoimmune disease. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2006;19(1):80-94. http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/CMR.19.1.80-94.2006. PMid:16418524.
Stéphan JL, Zeller J, Hubert P, Herbelin C, Dayer JM, Prieur AM. Macrophage activation syndrome and rheumatic disease in childhood: a report of four new cases. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1993;11(4):451-6. PMid:8403593.
Christen U, Edelmann KH, McGavern DB, et al. A viral epitope that mimics a self antigen can accelerate but not initiate autoimmune diabetes. J Clin Invest. 2004;114(9):1290-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1172/JCI200422557. PMid:15520861.
Kim YJ, Koo BS, Kim YG, Lee CK, Yoo B. Clinical features and prognosis in 82 patients with adult-onset Still’s disease. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2014;32(1):28-33. PMid:24050706.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Autopsy and Case Reports

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright
Authors of articles published by Autopsy and Case Report retain the copyright of their work without restrictions, licensing it under the Creative Commons Attribution License - CC-BY, which allows articles to be re-used and re-distributed without restriction, as long as the original work is correctly cited.